ASTM A106 vs A53 Grade B: Carbon Steel Pipe Guide
1. Introduction
In the field of industrial procurement, carbon steel pipe are widely used as basic materials for various projects, such as energy transmission, construction and chemical engineering. Among many standards, ASTM A106 and ASTM A53 are two most common specifications. However, many procurement professionals often find it difficult to tell the difference between the two. The core reason is that their chemical composition is similar-they are all low carbon steels, which have excellent machinability and weldability. What’s more, some pipes are even Dual Certified by two standards, which further increasing the confusion in material selection. Choosing the wrong type of carbon steel pipe may lead to high engineering costs, short service life and even potential safety hazards. Therefore, the purpose of this paper is to thoroughly clarify the differences between ASTM A106 and ASTM A53 from three core dimensions: chemical composition, manufacturing process and application scenarios. It will provide professional guidance for purchasing staff and project managers to make scientific and reasonable decisions.

2. What is ASTM A106 Grade B?
According to the official definition issued by ASTM International, ASTM A106 Grade B is defined as “seamless carbon steel pipe for high temperature”. A key feature different from other carbon steel pipe standards is that ASTM A106 Grade B is only a seamless pipe, and the welded versions is not included in this standard. The seamless manufacturing technology makes it have excellent structural integrity and consistency, and keeps its stable performance under extreme conditions.
In terms of chemical composition, ASTM A106 has strict requirements on silicon content, and there are minimum silicon content specification. Silicon plays an important role in improving the high temperature resistance of the steel, which enables the pipeline to resist oxidation and maintain mechanical strength even in high temperature environment. Its mechanical properties are also impressive: the yield strength is not less than 240 MPa, the tensile strength is between 415 MPa and 520 MPa, and the elongation is over 21%, which ensures its reliability under high pressure.
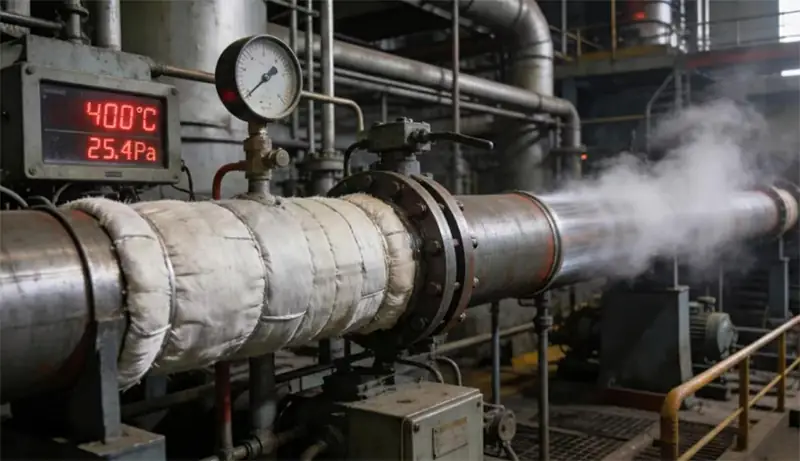
The core application scenarios of ASTM A106 are concentrated in the industrial environment of high temperature and high pressure. Typical applications include main steam pipelines of thermal power plants (working temperature is high temperature environments), the pipeline of hydrogenation unit of refineries and heat exchanger tube bundles of chemical plants. For example, in a supercritical power station project, ASTM A106 pipe with a wall thickness of 50 mm can withstand the working pressure of 25.4 MPa to ensure the safe and long-term operation of the power generation system.
3. What is ASTM A53 Grade B ?
Unlike ASTM A106, ASTM A53 has a wider definition. It is specified as “Standard Specification for Pipe, Steel, Black and Hot-Dipped, Zinc-Coated, Welded and Seamless”. This definition clearly indicates that ASTM A53 Grade B covers both seamless and welded carbon steel pipe, making it highly versatile in application.
ASTM A53 Grade B is divided into three main types based on manufacturing processes: Type F (Furnace Butt-Welded), Type E (Electric Resistance Welded, ERW), and Type S (Seamless). Among them, Type E (ERW) is the most widely used on the market. The ERW manufacturing process includes rolling steel strips into a circle, and then forming the pipe by resistance welding. This process is efficient, cost-effective, and suitable for mass production, which is why ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes (especially ERW pipes) occupy a large share in the carbon steel pipe market.
In terms of chemical composition, there is no minimum silicon content requirement for ASTM A53, which is a significant difference from ASTM A106. Its mechanical properties are slightly lower than those of ASTM A106 Grade B, with a yield strength of not less than 240MPa and a tensile strength of 415MPa to 515 MPa. However, these performance indicators are fully sufficient for most medium and low-pressure application scenarios.
ASTM A53 (especially the welded version) has a wide range of applications. It is mainly used for conveying low-pressure fluid, such as water supply and gas transmission pipelines in urban infrastructure. In addition, it is also widely used in structural support, such as scaffolding in construction projects, structural frames of large equipment and HVAC systems. For example, in the reconstruction project of urban water supply pipeline, ASTM A53 ERW pipes is widely used because of its cost-effectiveness and reliability.
4. The Key Differences
In order to help readers intuitively understand the differences between ASTM A106 and ASTM A53, the following table summarizes their core features:
| Comparison Items | ASTM A106 Grade B | ASTM A53 Grade B |
| Manufacturing Process | Seamless only; Manufactured by hot rolling or cold drawing, with no welding seams. | Seamless and welded (type E ERW is the most common); ERW process has high efficiency and is suitable for mass production. |
| Silicon Content | It has a minimum silicon content requirement for improving high temperature resistance. | There is no requirement for minimum silicon content; Chemical composition is flexible. |
| Application | High temperature and high pressure scene: steam pipeline in thermal power plant, hydrogenation unit in refinery, and high temperature reaction equipment in chemical industry. | Medium and low pressure fluid transportation (water and gas), building structure support, HVAC systems. |
| Price | Higher; Seamless manufacturing processes lead to complex production and higher costs. | Lowest (especially the welding version); ERW technology reduces production costs and has obvious price advantages. |
5. Why Choose A 53 (Welded) Instead of a 106?
Undeniably, ASTM A106 is irreplaceable in high temperature and high pressure environment. However, in most industrial projects, the working conditions have not reach such extreme levels. Blindly choosing ASTM A106 Grade B will only cause unnecessary cost increases. For general industrial applications, ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes is undoubtedly a more cost-effective choice.
First of all, in terms of cost control, the price advantage of ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes is extremely prominent. According to the Annual Report of Welded Pipe Market in 2025 published by Mysteel, the average price of welded pipes in China in 2025 was 3630 yuan/ton, while the price of seamless steel pipes was 269 yuan/ton higher than that of welded pipes. For large-scale projects that require a large number of carbon steel pipes, choosing ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes can save a substantial amount of procurement costs. At the same time, due to the mature and efficient ERW production process, ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipe has shorter delivery cycles, which can effectively speed up the progress of project construction.
Secondly, in terms of performance matching, ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes can completely meet the requirements of most low-pressure scenarios. For example, the working pressure of urban gas transmission pipeline is usually between 0.4 MPa and 1.6 MPa, and the tensile strength and yield strength of ASTM A53 are more than enough to ensure the safe operation of the pipeline. In terms of building and structural support, the excellent structural stability of ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes can provide reliable support for the whole structure.
As the market demand for cost-effective carbon steel pipe continues to grow, ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes have shown strong market competitiveness. Data shows that in 2025, the export of welded pipes in China is expected to exceed 6 million tons, with a year-on-year growth rate of 15%, and ASTM A53 welded pipes are an important part of these exports. This fully demonstrates that ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes has been widely recognized in the global market for its excellent cost performance and stable quality.
For general industrial use, structural applications, or low-pressure fluid transport, ASTM A53 Welded Pipe offers a more cost-effective solution.
6. FAQ
Q 1: Can ASTM A53 replace ASTM A106 in a high temperature environment?
A 1: no, ASTM A53 Grade B has no minimum silicon content requirement, so its high temperature resistance is obviously not as good as ASTM A106. Using ASTM A53 Grade B in high temperature and high pressure environment will lead to a sharp decline in performance and a safety hazards. ASTM A106 Grade B is the only choice for such scenarios.
Q 2: what are the advantages of ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes over seamless pipes?
A 2: the main advantages are low cost and short delivery time. The ERW manufacturing process of ASTM A53 welded pipes is more efficient and the utilization rate of raw materials is higher, which leads to the price being about 10% -20% lower than that of seamless pipes with the same specification. At the same time, it can realize mass production, and the delivery cycle is usually 3-7 days shorter than that of seamless pipes.
Q 3: is there any differences in the application of ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes in different areas?
A 3: the core performance of ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes conforms to the global ASTM standards, so its application scope is universal. However, in areas with harsh environmental conditions (such as extremely cold or highly corrosive areas), it may be necessary to carry out surface treatment, such as hot-dip galvanizing, to improve corrosion resistance and low-temperature toughness. At present, China’s ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes has been widely exported to Southeast Asia, the Middle East and other regions, and has well adapted to local working conditions.
7. Conclusions and CTA
In a word, ASTM A106 Grade B and ASTM A53 Grade B are two carbon steel pipeline standards with completely different positioning. ASTM A106 Grade B, as a seamless pipe for high-temperature and high-pressure services, is irreplaceable in scenarios such as thermal power plants and refineries. On the other hand, ASTM A53, especially its welded version, has the characteristics of cost-effectiveness, efficient production and wide applicability, making it the first choice for medium and low pressure fluid transportation and structural support projects. The core strategy for material selection is to “choose the right pipe for the right scene” -to avoid the waste caused by using high-cost ASTM A106 in ordinary scenes, and to use ASTM A53 in high temperature and high pressure environment will not affect the safety.
Do you need cost-effective steel pipes for your project? Contact Allland Steel Pipe today. We provide high-quality ASTM A53 Grade B welded pipes suitable for various structural and fluid applications. Our products strictly abide by ASTM standards, and have complete quality inspection reports and certification documents. Whether it is urban infrastructure construction, industrial fluid transportation, or other projects, we can provide you with professional material selection suggestions and reliable product supply.
Share:
Get Your Custom Steel Pipe Quote Today!
Provide us with your project details (like application, specifications, quantity). Our experienced team will respond with a tailored solution and competitive quote within 24 business hours.