Coated pipe: the core solution for industrial pipeline corrosion protection
(Introduction:In the field of industrial pipelines, corrosion is the main challenge threatening safety and lifespan, and steel pipe coated have become the mainstream choice to deal with this problem through efficient anti-corrosion technology.
(Purpose: This article focuses on the epoxy resin coating system, especially the FBE fusion epoxy process, analyzes its core advantages and application scenarios, and provides a concise and practical reference for pipeline corrosion protection.

I. Coated steel pipe: three core advantages
Coated pipe is a composite pipe with a protective layer coated on the surface of the steel pipe. The core advantages include:
· Life extension: By applying a 300-500μm coating (such as epoxy resin), the lifespan of ordinary steel pipes can be extended from 5-8 years to 20-30 years, significantly reducing replacement costs. It is a highly competitive and cost-effective choice.
· Scenario adaptation: From buried oil and gas pipelines, overhead fire protection systems to offshore platforms, it can adapt to more than 90% of corrosive environments.
· Cost optimization: The initial cost is 15%-30% higher than that of bare pipes, but the maintenance cost of the entire life cycle is reduced by 50%, and the long-term benefits are significant.
Ⅱ. Epoxy coating: the mainstream choice for industrial corrosion protection
1. Core technology and classification
**Epoxy coated pipe** uses epoxy resin as the base material and combines with steel pipe through molecular-level adhesion (≥50N/cm) to form a chemical and physical double barrier:
· Chemical corrosion resistance: can withstand strong media such as sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide, suitable for chemical and pharmaceutical industries;
· High temperature resistance: long-term use temperature ≤120℃, short-term withstand 200℃, performance is better than most coatings.
2. Two major types by different processes
· FBE fused epoxy coating: high-temperature melting powder process forms a seamless protective layer with strong anti-cathode stripping ability, which is the first choice for buried pipelines.
· Liquid epoxy coating: By adopting the room-temperature curing technology and applying it through spraying or brushing processes, a protective layer of 200-300μm can be formed without the need for high-temperature equipment. Its unique advantage lies in: construction flexibility; Fast curing High scene adaptability; The cost-effectiveness is 15%-20% lower than usual.
Ⅲ. FBE coating: the ultimate anti-corrosion solution for buried pipelines
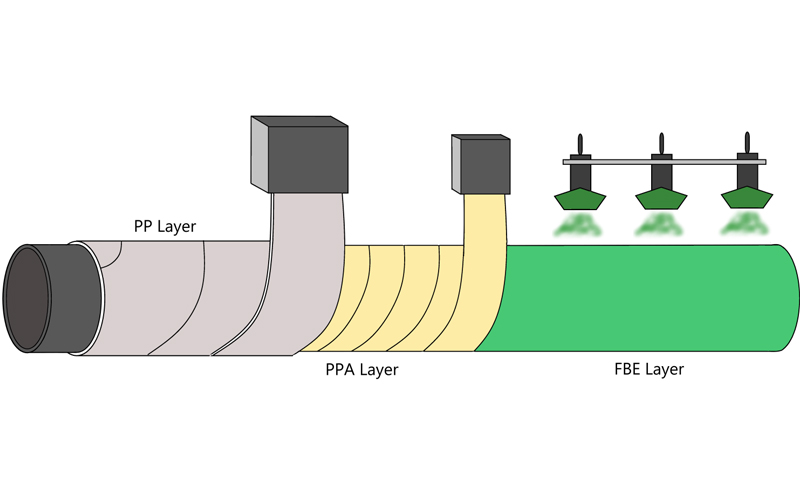
**FBE coated pipe** (fusion-bonded epoxy powder coated steel pipe) achieves ultimate anti-corrosion through a six-step strict process:
· Surface preparation
The steel sand/steel shot mixed abrasive was sandblasted to reach Sa2.5 grade (ISO 8501-1 standard), with a surface roughness of 50-75μm, forming a microscopic anchor pattern structure to ensure that the adhesion of the coating is ≥50N/cm² (ASTM D3359).
· Powder electrostatic spraying
The epoxy powder is charged by using a high-voltage electrostatic generator and evenly adsorbed onto the surface of the steel pipe to form a powder layer with an initial thickness of 150-200μm.
· Melt curing
The steel pipe enters the curing furnace at 230-250℃. The powder melts and flows out within 10-15 minutes, undergoing a cross-linking reaction to form a three-dimensional network structure. The final coating thickness is 300-500μm.
· Density testing
Direct current high-voltage electric spark leak detection (5-10kV) is adopted to detect coating leakage points (standard: ≤1 leakage point per square meter, and the hole diameter ≤0.3mm).
· Performance enhancement
Through secondary curing or post-treatment with ultraviolet light, the cross-linking density of the coating is increased, making the Shore hardness ≥D80 (ASTM D2240) and the wear resistance increase by 20%.
· Environmental protection closed loop
The recovered powder that not absorbed (utilization rate ≥95%) has no volatile organic compound emissions and complies with the ISO 14001 environmental management system.
IV. Key application scenarios

1. Energy and infrastructure
·!– /wp:paragraph –>
· Fire protection system: Epoxy coated steel pipes are resistant to moisture and prevent clogging of sprinkler heads, and are standard for fire protection in high-rise buildings;
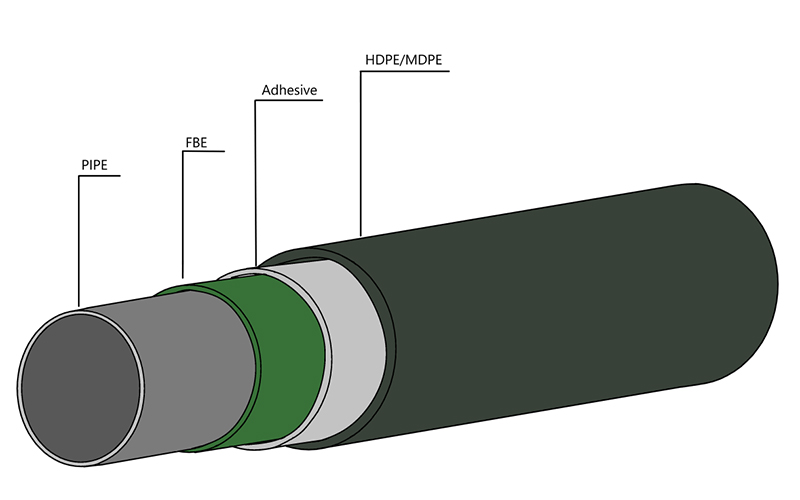
· Marine engineering: The three-layer structural coating (epoxy + polyethylene) resists salt spray and ensures that the South China Sea oil and gas platform has no major repairs for 20 years.
2. Core principles of selection
· Environmental adaptation: FBE (≥300μm) is selected for underground, liquid epoxy (200-300μm) is selected for overhead, and stainless steel substrate + epoxy is used for coastal areas;
· Cost balance: FBE (120-200 yuan/m) is selected for long-term projects, and liquid epoxy (100-170 yuan/m) is selected for short-term or renovation projects;
· Standard compliance: Refer to regional standards such as ASTM (North America), EN (Europe), and GB (China) to ensure project compliance.
Ⅴ. Conclusion: Choosing the right coating is the key to efficient corrosion protection
Pipe coated have become the core solution for industrial pipeline corrosion protection due to the technical advantages of epoxy coatings. Whether it is a long-term energy project or a construction project that focuses on cost-effectiveness, choosing a suitable coating process (FBE or liquid epoxy) is the key.
As a professional manufacturer, we provide a full range of coated steel pipes, covering DN15-DN1200, following international standards and supporting customized needs. Contact us now to get a selection guide to make pipeline corrosion protection more efficient and reliable.
Get Your Custom Steel Pipe Quote Today!
Provide us with your project details (like application, specifications, quantity). Our experienced team will respond with a tailored solution and competitive quote within 24 business hours.
Related Articles
ASTM A53 vs. API 5L: A Guide to Selection and Application
Introduction:Technology differences determine success or failure, and selection needs to be “precise”
Steel Density Analysis: Core Differences between Mild and Medium Carbon Steels and Industrial Applications
3LPE coated steel pipe: a solid barrier in the field of industrial corrosion protection
3LPP coated pipe: anti-corrosion guard in high temperature and high pressure environment
FBE steel pipe: the technological armor of the steel defense line
HOT TAGS
latest posts
- How LSAW/SSAW Steel Pipes Ensure Safe & Durable Drinking Water Pipelines
- LSAW steel pipe vs ERW steel pipe: Unveiling Core Process Differences in Steel Pipe Welding from Arc to Current
- The Essential Guide to High Pressure Pipe Applications
- API 5L Grades Explained: X52, X65 & X70 Meaning?
- A Guide to Offshore Steel Pipe & Tubes for Subsea Projects